|
CHAPTER 6 : SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
Tuesday, 27 October 2015 @ 19:24
SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE
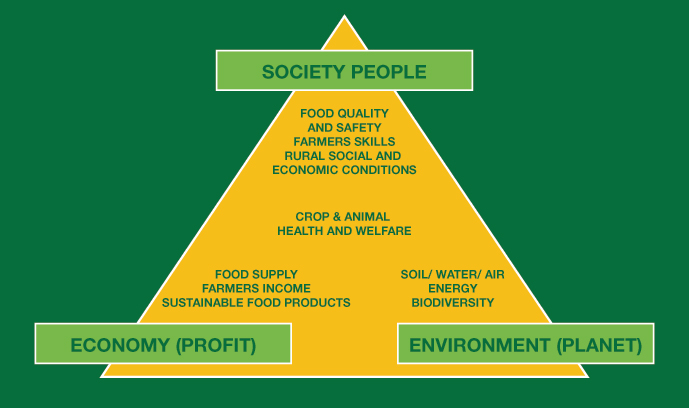
Farming system that are capable of maintaining their productivity to society indefinitely without causing irreversible damage to ecosystem health.3 MAIN GOALS OF SUSTAINABLE AGRICULTURE 1. ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT 
Policy intervention endeavor with aims of economic and social well-being of people, economic growth is a phenomenon of market productivity and rise in GDP. Consequently, as economist Amartya Sen points out, "economic growth is one aspect of the process of economic development".
Farming can generate financial for family and decrease their debt. It also make us to be less reliance on government subsidies and external purchase of feed and fertilizers.
The type or new techniques that can be applied under profitable enterprises are alternative crops such as herbs and mushrooms, mixed cropping, integrating plant and animal production, contract farming and organic farming.
2. ENVIRONMENTAL CONSERVATION

The effective water cycles involved fast entry of water to soil and capacity of soil to store large amount of water. These can be achived by managing good irrigation and keep soil covered with plants or mulch.

Well functioning mineral cycle is when there is smooth movement of nutrients from soil => crops & animals => soil and low requirement of fertilizers and feed.
Effective ecosystem dynamics have large diversity of plants and animals both above and below the ground. The strategies in ecosystem dynamics are :
- Intercropping

Multiple cropping practice involving growing two or more crops in proximity.
- Crop Rotation

Crop rotation is also used to control pests and diseases that can become established in the soil over time. The changing of crops in a sequence tends to decrease the population level of pests. Plants within the same taxonomic family tend to have similar pests and pathogens.
- Cover Crops

Cover crops are plants seeded into agricultural fields, either within or outside of the regular growing season, with the primary purpose of improving or maintaining ecosystem quality.
- Compost & Fertilizers

Compost is organic matter that has been decomposed and recycled as a fertilizer and soil amendment. Compost is a key ingredient in organic farming.
- Tillage

Tillage is the agricultural preparation of soil by mechanical agitation of various types, such as digging, stirring, and overturning. Examples of human-powered tilling methods using hand tools include shovelling, picking, mattock work, hoeing, and raking.
- Zero Burning

The zero burning replanting is a practice in which the old and uneconomical standards of oil palm and other tree corps are felled and shredded and left to decompose in situ This technique also allows all plant tissues to be recycled, enhancing soil organic matter.
- Pest Management

3. SOCIO-POLITICAL BENEFITS 
This sustainable agriculture gives benefits to socio-political by providing social benefits to farm family and community. The money is kept circulating in the community (for examples : buying supplies locally rather than ordering out of state). It involves marketing strategies which is direct marketing through farmers markets or road side stalls. And lastly, by choosing and supporting loca producers, the payment can be cut off a little.
newer post ★★★
older post
|
 |